Solving Banks’ Liquidity Challenge
April 08, 2020
Pressure on core deposit growth
Recent articles in the banking press indicate the growth of digital banks and their function in providing core deposits for their parent financial institutions. Consider the following:
“With new digital bank, RBC joins a crowded field.”
American Banker, February 25, 2020
“Direct banks deposit growth and market domination.”
Banking Strategies, November 11, 2019
“How MUFG’s ‘digital hybrid’ bank raised $7B in deposits”
American Banker, July 11, 2019
“Disrupting finance: Digital banks offer a more compelling digital banking experience”
Forrester, May 2019
Smaller banks in particular are facing liquidity challenges. Their share of total deposits continues to shrink when compared to global banks as shown in the most current data from the FDIC. Additional research from Darling and Associates, suggests banks under $10 billion in assets have not grown core deposits sufficiently to fund loans for the past three years
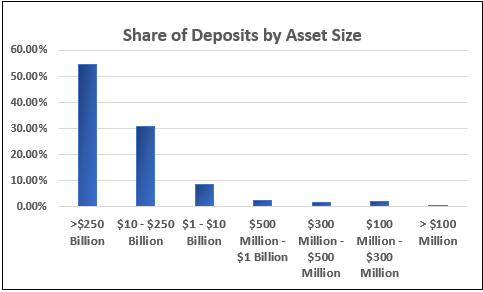
Opening a new branch, offering new account opening functionality or operating a 24/7 call center provide short-term tactics to gain deposits. More impactful and sustainable solutions are desirable for executives seeking longer term solutions, particularly in a digitally enabled world. A direct bank offers such a long-term solution, and retail customers are ready and willing to bank in this fashion.
Consumers desire direct banking
According to recent findings from the FIS Performance Against Consumer Expectations (PACE) survey, direct banks are gaining traction versus traditional financial institutions.
- Customer satisfaction with direct banks surpassed global banks, regional banks and credit unions for the first time in the 2020 survey.
- Senior millennials (age 29-39) are 300 percent more likely than Gen Xers (39-55) to be direct bank customers.
- Direct bank customers are most likely to have a smart phone and least likely to visit an ATM.
Bank customers want:
- Better banking experiences
- Access via mobile devices
- More favorable interest rates
Seeking a new way to stand up a direct bank
Multiple paths are available for community banks to participate in direct banking. Some banks launch direct banks under their current platforms as extensions of their traditional banks. Less expensive to launch on the front end, this option, however, has downsides, including: challenges presented by coordinating changes for two banks on one platform to support two different businesses, and increased pressure on employees to manage both those businesses in parallel. Leveraging the current platform may also hamper the bank’s ability to optimize brand positioning to attract new segments.
Community banks also can engage in partnerships with fintechs to participate in direct banking. In this scenario, the bank loans out its charter to the fintech in order to capture new income streams. This approach avoids disruption to banking operations but can stymie a bank’s ability to extend its own market presence as the customer relationship is typically controlled by the fintech in these types of engagement models.
A third option is to deploy direct banking capability on a different platform – on-demand core solutions that offer turnkey software options enabling the rapid deployment and launch of direct banking on a lightweight platform. When evaluating potential providers of turnkey options, bankers should look for these attributes:
- An end-to-end integrated solution that is fully SaaS/cloud-based
- An extensible (to all devices and channels) and scalable (addressing volume and complexity) offer
- A truly digitally oriented environment
- The ability to deploy and launch quickly
- A cost-effective solution
Core on demand approach delivers meaningful benefits
This third option – on-demand core – allows for rapid implementation and launch of a direct bank with a different approach to more methodical step-by-step programs, encouraging agility and rapid delivery of banking services. This speed and flexibility enable the capture core deposits more sustainably than traditional methods. The benefits of this approach include:
- Cost economies – Real-time processing capabilities that deliver true market advantage without the high cost and without compromising on functionality.
- Increased efficiencies – As a separate core solution, integration and interaction with a bank’s existing core is not a complicating factor
- Speed to market – Innovation is not hampered by the limitations of existing legacy systems.
- Uninterrupted growth – 24/7 capabilities reduce operational risk and create an always-on solution for a community institution and its direct banking customers.
- Rapid deployment – The core’s cloud-native architecture allows fast deployment of a direct bank – as soon as 90 days.
Rapid execution for deposit growth
Direct banks fuel deposit growth. The potential to rapidly drive deposit growth and support improved deposit/loan ratios for a financial institution is the primary driver behind the surge in direct banks. By leveraging a robust portfolio of services, including a real-time core processing engine, security and fraud prevention systems, it has been shown that institutions can launch direct banks at scale and grow deposits into the billions in a matter of months.
The technology and tools are available today to build a digital-only bank for community banks quickly. The successful launch of a direct bank hinges on the ability to embrace new technology and a willing executive management team at the institution. Executing a sound direct bank plan will meet the business requirements a traditional financial institution, while positioning the bank for a more robust digital banking future.
- Topics:
- Digital transformation
