Hybrid Design Leveraging Native Controls Optimizes Mobile Banking
November 13, 2019
Optimizing the mobile user experience is now table stakes in attracting and retaining customers as big banks offer fully featured mobile apps. Taking a cue from other industries, consumers expect to be able to do everything on their mobile devices that they can do online.
Four ways that mobile banking apps fail
Often, banking apps fail to gain traction because they create obstacles to achieving the convenience and ease of use that consumers demand in these ways:
- Some designs offer a cool-looking interface but fail to provide satisfying user experiences. A pretty face cannot overcome irritation created by inadequate usability.
- Many banking apps are designed to supply a subset of online features instead of being designed to be “mobile first” and fully featured with all of the functions available in other self-service channels.
- Banking apps that don’t leverage the native capabilities inherent in the mobile phone produce suboptimal experiences. For example, when remote deposit capture was initially introduced, it relied on the customer to provide a clear enough check image to be accepted for deposit instead of tapping into the mobile phone’s autofocus capability. As a result, consumers’ “fuzzy photos” were often rejected multiple times.
- Banking apps that fail to enable the integration of competitive apps – for example, Venmo or PayPal – steer customers away and toward competition.
Optimize mobile banking interactions
Optimizing mobile banking interactions pivots around two factors – tapping into native capabilities by leveraging existing platform standards as much as possible and then extending capabilities through hybrid features.
Using native controls provides several key advantages. First, the app replicates how consumers are already habituated to using various mobile phone features such as the camera or biometrics capabilities – thus, no additional user training is required. Using native controls also enables customers to take advantage of accessibility features of the operating system – for example, enlarging text for improved readability. Third, native controls are more responsive – providing improved performance – than non-native capabilities.
A hybrid design extends the features and functions of the mobile phone to deliver an experience that parallels any other self-service channel and provides customers with easy access to their accounts at any time and from anywhere. Since many hybrid experiences utilize web-based technology, features can be designed and developed quickly. However, these capabilities that are used to extend reach are less responsive than native controls. As a result, they are optimally applied to less frequent actions such as reordering checks, opening or closing an account, or resetting a password.
Then, now and in the future
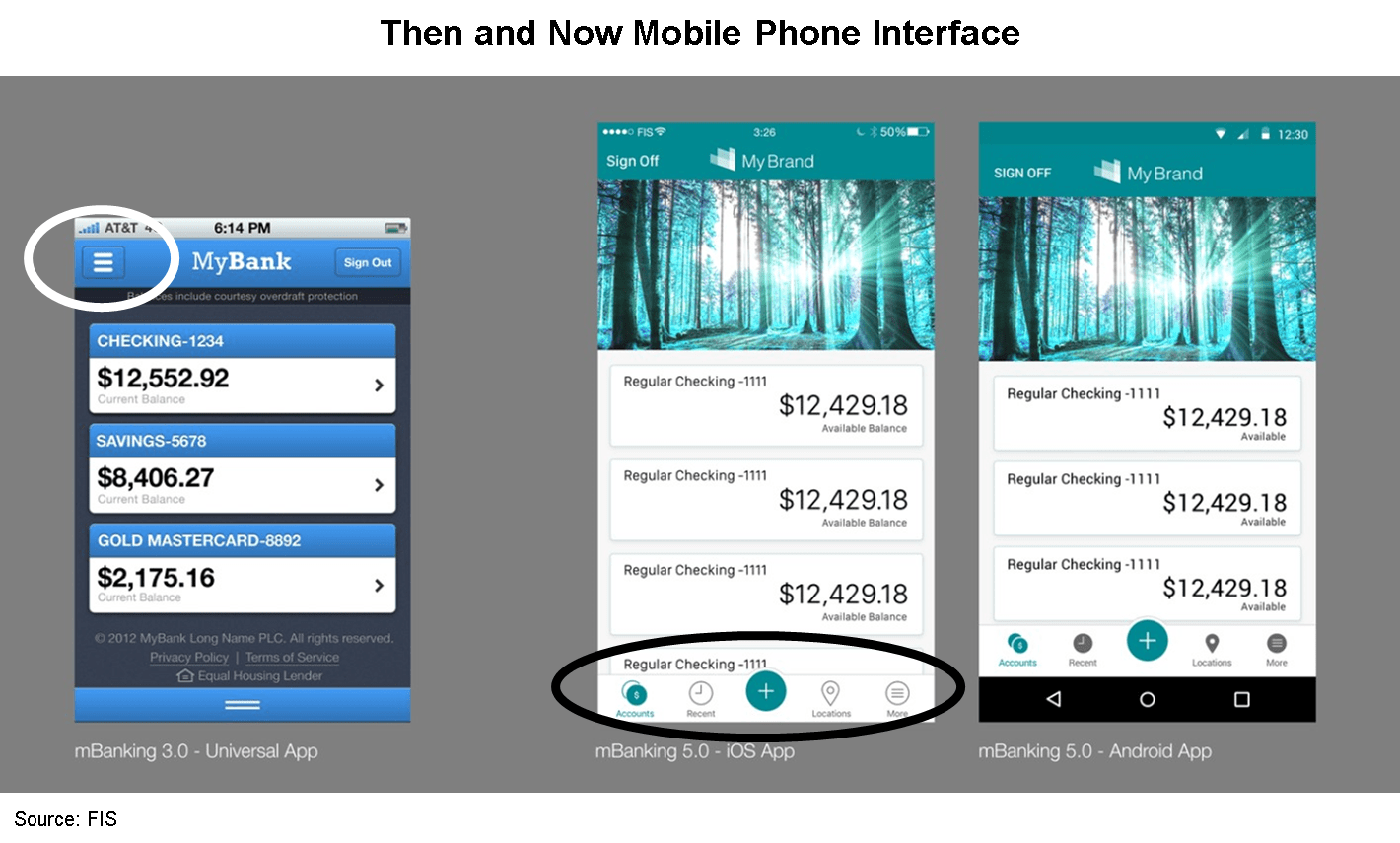
“Now design” leverages a tab bar to prominently display navigation features in lieu of tucking them under the “hamburger menu” highlighted on the left.
In the future, customers will expect even greater personalization of user interfaces to reflect the way they live their lives. For example, features that reflect individuals’ priorities may be accessed through a dashboard that provides a holistic view of one’s finances. Also, expect more contextual awareness to be built into banking apps – for example, signaling customers who consent to geolocational alerts when they are near a cardless cash ATM or near a frequently shopped store that’s holding an event.
Mobile banking is now the way that the majority of consumers engage most often with their financial institutions. Make sure that your mobile banking app is fully featured for all self-service tasks and is designed to prioritize ease of interaction.
- Topics:
- Digital transformation
